Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language known for its simplicity, readability, and versatility. It has a rich ecosystem of libraries and frameworks that support a wide range of applications, from web development and automation to data science, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and more. Here's why Python has a bright future:
1. Simplicity and Readability
Python’s syntax is clean and easy to learn, making it a great language for beginners. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability and reduces the complexity of writing programs. This simplicity leads to faster development cycles and is one of the reasons why Python is popular in educational settings.
2. Versatility and Wide Adoption
Python can be used for a variety of applications:
Web development: Frameworks like Django and Flask enable rapid development of web applications.
Data Science & Machine Learning: Libraries like NumPy, pandas, TensorFlow, and scikit-learn make Python the go-to language for data **** ysis, statistical modeling, and AI.
Automation: Python is often used to write scripts for automating repetitive tasks, making it popular in IT and operations.
Software Development: With tools like PyQt and Kivy, Python can also be used to develop cross-platform desktop applications.
3. Large Ecosystem of Libraries and Frameworks
Python has a vast repository of third-party libraries available through the Python Package Index (PyPI). These libraries allow developers to quickly implement complex functionalities without having to write everything from scratch.
4. Strong Community and Support
Python has a large, active, and vibrant community of developers. This means extensive documentation, tutorials, forums, and user-contributed packages. Community-driven development also ensures that Python remains updated and adaptable to new technologies.
5. Cross-Platform Compatibility
Python is cross-platform, meaning it runs on various operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. This flexibility ensures that developers can deploy their applications in a variety of environments without having to rewrite the code.
6. Growing Demand in Emerging Technologies
Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML): Python is the most commonly used language in AI/ML development. Its libraries and frameworks are highly optimized for data processing and building machine learning models.
Data Science and **** ytics: Python's strong data manipulation libraries (e.g., pandas, NumPy, and matplotlib) make it the preferred choice for data **** ysts and scientists. With the explosion of big data, Python is central to **** ytics.
IoT (Internet of Things): Python is increasingly used in IoT projects due to its ease of use, flexibility, and compatibility with hardware like Raspberry Pi.
7. Performance Improvements
While Python is not the fastest language due to being interpreted, the performance gap has been closing. Tools like PyPy (a just-in-time compiler) and Cython (which allows writing C extensions for Python) allow developers to speed up critical parts of their applications. Additionally, Python’s integration with other languages, like C or Java, helps improve performance when needed.
8. Corporate Support
Major tech companies like Google, Facebook, NASA, and Spotify use Python in various capacities. The backing of these organizations provides stability to the language and ensures it remains a valuable skill in the job market.
9. Ease of Integration
Python integrates well with other languages and technologies. For instance, it can call C/C++ libraries for performance-heavy tasks, interface with Java applications, or communicate with web services via APIs. This makes Python suitable for a wide range of applications and use cases.
10. Educational Use and Adoption
Python is frequently used to teach programming concepts at universities and coding boot camps. Its simplicity and broad use in real-world applications mean that new generations of developers are often introduced to it early in their careers.
11. Global Popularity and Career Opportunities
Python is consistently ranked as one of the most popular programming languages in the world, and job demand for Python developers remains high. It’s especially prominent in fields like data science, AI, web development, and automation.
Conclusion: The Future of Python
Python’s future looks bright because it continues to evolve with the demands of the technology landscape. Its role in fields like AI, machine learning, data science, and automation will only increase, and its simplicity and readability will continue to make it a favorite choice for both beginners and experienced developers. As long as it maintains its strong community support and adapts to emerging trends, Python will remain a central player in the programming world.
https://www.python.org/
1. Switch to Cleaner Fuels
Low-Sulfur Fuels: The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has implemented regulations to reduce sulfur emissions. Ships can use low-sulfur fuels (like Very Low Sulfur Fuel Oil - VLSFO) instead of traditional high-sulfur bunker fuel.
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG): LNG is a cleaner alternative to conventional marine fuels as it significantly reduces emissions of CO2, sulfur oxides (SOx), and nitrogen oxides (NOx).
Biofuels: Some ships are beginning to use biofuels made from renewable sources like algae, waste oils, or plant-based materials, which have a lower carbon footprint.
Ammonia and Hydrogen: Though still in the experimental stage, ammonia and hydrogen have the potential to be carbon-free fuels when produced from renewable sources.
2. Energy Efficiency Measures
Hull Design & Maintenance: Modern hull designs, such as those with smoother surfaces and more hydrodynamic shapes, can reduce drag and fuel consumption. Regular cleaning and maintenance of the hull can also help maintain fuel efficiency.
Energy-saving Devices (ESDs): These include air bubble systems, ducts, and fins that improve the flow of water around the ship, reducing resistance and energy consumption.
Wind Propulsion Technologies: Technologies like sails, kite sails, and rotor sails harness wind energy to reduce the reliance on engines and reduce fuel consumption.
Energy-Efficient Engines: Newer, more efficient engines consume less fuel and emit fewer pollutants. Engine tuning, regular maintenance, and using low-load engines (engines optimized for slower speeds) can also improve energy efficiency.
3. Use of Scrubbers and Exhaust Gas Cleaning Systems
Scrubbers: These are devices installed on the exhaust stacks to remove sulfur oxides (SOx) and other pollutants from ship emissions. Scrubbers can clean exhaust gases, allowing ships to burn higher sulfur content fuel while meeting emission regulations.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR): EGR systems reduce NOx emissions by recirculating part of the exhaust back into the combustion chamber, reducing the formation of NOx during combustion.
4. Operational Efficiency and Best Practices
Slow Steaming: Reducing the speed of a ship, a practice known as slow steaming, reduces fuel consumption and emissions. Lower speeds also decrease the energy required to overcome hydrodynamic resistance.
Weather Routing: Using weather data and forecasting tools to optimize a ship's route can reduce fuel consumption and emissions by avoiding adverse weather conditions (e.g., headwinds) and taking advantage of favorable currents.
Port Time Optimization: Efficient port operations, such as reducing the time ships spend waiting at ports or idling, can also lower emissions. Strategies like cold ironing (using shore power while docked) allow ships to turn off engines while in port, reducing the use of auxiliary engines that produce emissions.
5. Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
Though still in the early stages, the concept of carbon capture and storage for ships involves capturing CO2 emissions from the exhaust gases and storing them safely, preventing their release into the atmosphere. This is still an emerging technology for the maritime industry.
6. Alternative Propulsion Technologies
Electric Propulsion: The use of batteries or fuel cells for electric propulsion is gaining attention, especially for short-sea shipping and ferries. These vessels rely on electricity stored in batteries or generated on board through renewable energy sources.
Hybrid Systems: Hybrid propulsion systems combine traditional internal combustion engines with batteries or fuel cells, allowing for reduced emissions during certain parts of the voyage (e.g., port entry, and docking).
7. Compliance with International Regulations
IMO 2020 Regulation: The International Maritime Organization (IMO) introduced the IMO 2020 sulfur cap, which limits the sulfur content in marine fuels to 0.5% globally (down from 3.5%). This has encouraged the use of low-sulfur fuels or the installation of scrubbers.
IMO’s GHG Strategy: The IMO has set a goal to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from shipping by at least 50% by 2050 (compared to 2008 levels). This includes measures such as reducing carbon intensity (CO2 per ton-mile) and encouraging the use of zero-emission fuels.
8. Research and Development of Innovative Technologies
Investment in R&D for new technologies, including carbon-neutral fuels, improved propulsion systems, and advanced emissions abatement technologies, will be essential to achieving long-term reductions in ship emissions.
Collaborative efforts between shipping companies, fuel suppliers, technology providers, and regulatory bodies can speed up the development of these innovations.
Reducing ship emissions involves a combination of technological advancements, operational efficiencies, and the use of cleaner fuels. The maritime industry is increasingly moving toward a sustainable future, driven by stricter environmental regulations and the growing demand for environmentally responsible practices. By adopting these strategies, the shipping industry can significantly reduce its environmental footprint and contribute to global efforts in tackling climate change.
https://www.goltens.com/pr...
Major Events That Influence Cryptocurrency Fluctuations:
Government Regulations and Policies:
Regulation of Cryptocurrencies: Government decisions on how cryptocurrencies are regulated can have a significant impact on their value.
For example:
Stricter Regulations: If governments impose stricter rules on crypto exchanges, taxation of crypto transactions, or AML/KYC (Anti-Money Laundering/Know Your Customer) requirements, it could create uncertainty and cause market volatility.
Clearer Regulations: On the other hand, clear, crypto-friendly regulations can help legitimize the market and increase adoption.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): The development and potential launch of government-backed digital currencies could challenge or complement existing cryptocurrencies.
Macroeconomic Events:
Interest Rate Changes: When central banks (such as the U.S. Federal Reserve) raise or lower interest rates, it can influence risk appetite in the financial markets. Cryptocurrencies are often seen as higher-risk ****** ets, so rate hikes (which make traditional investments more attractive) can lead to a decrease in crypto prices, while rate cuts may have the opposite effect.
Inflation: Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are often seen as a hedge against inflation, so high inflation may lead to an increase in demand for digital ****** ets. Conversely, stable or low inflation could reduce crypto’s appeal as an inflation hedge.
Technological Advancements:
Improvements in Blockchain Technology: Advances such as Ethereum's transition to proof-of-stake (PoS) or enhancements in scalability and transaction speed can lead to increased confidence in the technology, boosting the value of ****** ociated cryptocurrencies.
Security Vulnerabilities: On the flip side, if a major cryptocurrency hack or vulnerability is exposed, it could lead to panic selling and a temporary decline in the market.
Market Sentiment:
Investor Sentiment and Media Influence: Crypto markets are highly driven by sentiment. Positive news, like institutional investment (e.g., Tesla buying Bitcoin) or celebrity endorsements, can trigger surges in prices, while negative news (e.g., exchange hacks, fraud cases, or regulatory crackdowns) can lead to sharp declines.
Social Media Influence: Platforms like Twitter, Reddit, and others have shown that viral trends and influencer opinions can lead to massive fluctuations in the crypto market (e.g., the rise and fall of Dogecoin or Shiba Inu).
Geopolitical Events:
Political Instability: Geopolitical tensions, such as wars, trade disputes, or political crises, can make cryptocurrencies more attractive as a safe haven ****** et. This was seen with Bitcoin and Ethereum prices rising during times of geopolitical uncertainty, as investors looked for alternatives to traditional fiat currencies.
Legal Tender Adoption: If countries adopt Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies as legal tender (like El Salvador did with Bitcoin), it could legitimize crypto ****** ets in the global economy and lead to a price surge.
Potential Impact of Trump’s Win on the Crypto Market:
Pro-Business and Deregulatory Stance:
Pro-Crypto Policy: Trump has often been pro-business and may take a more deregulatory approach towards cryptocurrencies, which could benefit the market. If his administration were to ease regulations on crypto exchanges, or if he advocated for lower taxes on cryptocurrency gains, it could lead to a surge in institutional and retail investment in digital ****** ets.
Positive Impact: A pro-business, pro-crypto environment could increase confidence in the market, leading to higher demand, especially from institutional investors looking for opportunities in a less regulated environment.
Example: When the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) or other regulators take a more hands-off approach to cryptocurrencies, it can allow businesses to innovate without fear of heavy penalties or restrictions, making it easier for crypto-related projects to grow.
Inflation and Debt Concerns:
Currency Devaluation: If Trump's economic policies led to higher government spending or increased national debt, it might prompt inflationary pressures. Many see Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies as a hedge against inflation, so an increase in inflation or a weakened U.S. dollar under Trump’s policies could spur more demand for digital ****** ets, particularly Bitcoin.
Positive Impact: If inflation fears rise under Trump’s administration, more investors might flock to crypto as a store of value, especially in light of concerns about fiat currency devaluation.
Regulation of Stablecoins and CBDCs:
Trump’s administration might introduce policies around stablecoins and the potential launch of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs).
Stablecoins like Tether (USDT) or USD Coin (USDC) are linked to fiat currencies like the U.S. dollar. If Trump’s government creates favorable policies for stablecoins, their use could become more widespread, which might positively impact the crypto market.
CBDCs could compete with decentralized cryptocurrencies. If Trump were to support a U.S. CBDC in response to growing demand for digital currencies, this might lead to competition with private cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Neutral to Negative Impact: Depending on how CBDCs are implemented, it could diminish demand for decentralized cryptos if people prefer government-backed digital currencies that offer stability and official backing.
Potential for Increased Adoption:
If Trump pushes for the legalization of crypto investments or allows more crypto-friendly taxation policies, it could help accelerate mainstream adoption in the U.S. This might attract more institutional investors, especially in a global economic environment where inflation and fiat currency risks are top concerns.
Positive Impact: More institutions and large financial entities entering the crypto ****** e, backed by clear regulatory frameworks, could fuel long-term growth in the crypto market.
Potential Anti-Crypto Sentiment:
On the flip side, Trump might take a more cautious stance on cryptocurrencies if he sees them as a threat to traditional financial systems or government control over monetary policy. His administration could adopt more restrictive measures for crypto exchanges, enforce more scrutiny on crypto transactions, or even ban certain activities related to crypto (though this is less likely given his pro-business approach).
Negative Impact: A crackdown on crypto could lead to a decline in market sentiment, particularly if regulations limit crypto trading, mining, or its use in everyday transactions.
Conclusion:
If Donald Trump were to win the 2024 election, the cryptocurrency market could experience both positive and negative impacts, depending on the specifics of his policies. On one hand, a pro-business and deregulated stance could encourage more investment in digital ****** ets, leading to a bullish market for crypto. On the other hand, potential regulatory restrictions, particularly concerning stablecoins or CBDCs, could create uncertainty and lead to short-term market downturns.
Ultimately, the direction of the market will depend on how Trump’s administration handles issues like taxation, financial regulation, and the role of cryptocurrency in the global economy. The general market sentiment will also play a crucial role, as crypto markets are highly reactive to both political and economic changes.
https://www.bbc.com/news/a...
US shares, Bitcoin hit record high and dollar soars on Trump win
The result could have a far-reaching implications for tax and trade policy, as well as economies around the world.
https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/c6246e3w935oOn October 28, 2023, the Maritime and Port Authority of Singapore (MPA) reported that 5 tonnes of oil had spilled into the sea off the coast of Changi, a region located on the eastern side of Singapore's main island. The MPA confirmed that the overflow has ceased, meaning the source of the spill was contained and no further oil was being released. While the precise details of the incident are still under investigation, here’s an overview of what likely happened, potential parties that could be responsible, and the environmental impacts of such a spill:
What Likely Happened:
The oil spill occurred in Singapore’s busy waters near Changi, which is a significant location for shipping and port activities.
The spill was reported to involve 5 tonnes of oil, a relatively small but still concerning amount, especially in a delicate marine environment like Singapore's.
The source of the spill could have been a maritime accident, such as a collision between ships, a leak from a vessel's fuel tank, or a malfunction in an oil storage or transport system.
The MPA stated that the overflow ceased, which typically means that whatever caused the spill (such as a leak or accident) was shut off or contained before more oil could be released into the water.
Who is Likely Guilty?
Determining guilt in such cases usually depends on an investigation by local authorities (MPA, police, or environmental agencies), but potential parties that could be held responsible include:
Shipping Companies or Operators:
If the spill was caused by a ship collision or a faulty fuel line, the company responsible for the ship or vessel involved could be found guilty. This could include:
Negligence in maintenance: If the ship’s operators didn’t properly maintain equipment or manage fuel systems.
Navigational errors: If a ship caused the spill due to a mistake in navigation or collision with another vessel or structure.
Failure to follow safety procedures: If safety protocols for handling or transferring oil were not followed.
Port Facilities or Oil Operators:
If the spill occurred during oil transfer operations at the port, facilities managing oil storage or cargo handling could be held responsible for not properly securing tanks or pipelines, leading to a spill.
Human Error or Mechanical Failure:
In some cases, spills are the result of a combination of human error or equipment malfunction, such as a failure to properly shut off valves during an operation or faulty equipment that causes an overflow.
Given that Singapore has stringent regulations governing oil spills and maritime operations, the investigation will likely focus on identifying whether there was negligence or non-compliance with environmental and safety regulations.
Impact on the Environment:
Marine Life and Ecosystems:
Even though 5 tonnes may sound small in comparison to large-scale spills, it can still have a significant impact on marine life, especially in a sensitive area like Changi. The spill could affect local fish, coral reefs, marine birds, and mollusks.
Oil is toxic to marine organisms. It can contaminate food sources, coat the feathers of birds and the fur of marine mammals, and poison fish and other sea creatures through ingestion and absorption.
Smothering: Oil slicks can cover and suffocate the marine plants and animals that are vital to the food chain. Coral reefs, in particular, are highly sensitive to oil contamination and can be severely damaged, leading to long-term ecological damage.
Water Quality:
The oil could degrade water quality, making it unsafe for both marine life and humans. It could lead to long-lasting contamination of the marine ecosystem, especially if the oil reaches shorelines or beaches.
Air Pollution:
In some cases, when oil is not properly cleaned up or contained, it can evaporate and release toxic fumes, leading to air pollution around the affected area.
Cleanup Challenges:
The spill will require extensive cleanup operations. While the MPA has not reported the full scope of the efforts, cleaning up even a small spill like this can be difficult and costly. Oil slicks are challenging to remove, and they often require specialized equipment and techniques, such as booms (floating barriers), skimmers (to remove oil from the water’s surface), and dispersants (chemical agents that break down the oil).
The effectiveness of the cleanup efforts will depend on weather conditions, the spread of the oil, and the speed at which the oil is contained.
Long-Term Environmental Consequences:
Persistent contamination of the marine environment, such as damage to coral reefs or mangrove ecosystems, could have long-lasting effects on local biodiversity.
While some marine species can recover from oil contamination, the recovery time can take years, and the damage to ecosystem services (e.g., fisheries, tourism) can have economic implications for the region.
Next Steps and Consequences:
Investigation:
The MPA and other authorities will likely conduct an investigation to determine the exact cause of the spill, who is responsible, and the extent of the damage. If negligence is found, penalties may be imposed, including fines or compensation for the cleanup costs.
Legal Action:
If a party is found to be at fault, they could face legal action, including fines or lawsuits for violating environmental protection laws or failing to adhere to safety regulations.
Preventative Measures:
This incident may prompt stricter regulations or safety measures for oil-handling procedures in the area, especially for maritime operations around Singapore’s busy port. It could also lead to increased monitoring of ships and oil terminals.
Conclusion:
While the 5-tonne oil spill off Changi on October 28, 2023, might seem small, it still poses serious risks to the environment, especially to marine ecosystems in the region. The investigation will determine who is at fault, and depending on the findings, the responsible parties could face legal or financial penalties. The spill’s impact on local marine life and water quality will likely prompt an ongoing cleanup effort to mitigate environmental damage.
https://www.theonlinecitiz...

MPA reports 5 tonnes of oil spilled off Changi on 28 Oct; Overflow has ceased - The Online Citizen
The Maritime and Port Authority of Singapore (MPA) updated on the oil spill incident off Changi at 5.40pm on 28 October. During a bunkering operation with the Bahamas-flagged bulk carrier INES CORRADO, around five tonnes of oil overflowed into the sea. As of 8am on 29 October, no oil was spotted, an..
https://www.theonlinecitizen.com/2024/10/29/mpa-reports-5-tonnes-of-oil-spilled-off-changi-on-28-oct-overflow-has-ceased/Basic Principle of Air Conditioning:
An air conditioner cools indoor air by transferring heat from the inside of a building to the outside, using a process called heat exchange. Essentially, it moves warm air out and circulates cooler air in, creating a comfortable indoor environment.
Key Components of an Air Conditioner:
Refrigerant:
The refrigerant is a special fluid (often gas or liquid) that absorbs and releases heat as it circulates through the air conditioner. It goes through a cycle of evaporating and condensing to facilitate this process.
Compressor:
The compressor is usually located outside the building, and it pumps the refrigerant gas under high pressure. When the refrigerant is compressed, it heats up significantly.
Condenser Coil (outside unit):
The condenser coil releases the heat that was absorbed by the refrigerant. As the hot, high-pressure refrigerant gas moves through the condenser coil (which is located in the outdoor unit), it cools down and condenses into a liquid.
Expansion Valve:
The expansion valve (also known as a metering device) is located between the condenser and the evaporator. It regulates the flow of the refrigerant into the evaporator, causing it to expand and lose pressure. This allows the refrigerant to cool down further before it enters the evaporator coil.
Evaporator Coil (indoor unit):
The evaporator coil is located inside the building, usually in the air handler or the furnace unit. Here, the cooled refrigerant absorbs heat from the indoor air. As the refrigerant evaporates (changes from liquid to gas), it absorbs heat, thus cooling the air around the coil.
Blower Fan:
The blower fan pushes warm indoor air over the evaporator coils. As air passes over the coils, it cools down, and the now-cooler air is blown back into the room or ******* e.
Thermostat:
The thermostat senses the temperature of the air and adjusts the operation of the air conditioning system. When the room reaches the desired temperature, the thermostat signals the system to turn off.
How the Process Works Step by Step:
Warm Air is Drawn In:
Warm air from the room is sucked into the air conditioner through a return vent.
Cooling the Air:
The air passes over the evaporator coil, which contains cold refrigerant. As the warm air flows over the coil, the refrigerant inside absorbs the heat, cooling the air. The now-cool air is then blown back into the room by the blower fan.
Heat Absorbed by Refrigerant:
Inside the evaporator coil, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the warm air, causing the refrigerant to evaporate (turn from liquid to gas).
Refrigerant Moves to the Compressor:
The refrigerant gas is then pumped to the compressor located in the outdoor unit, where it is compressed under high pressure. This increases the temperature of the refrigerant gas.
Heat is Released Outside:
The high-pressure, hot refrigerant gas then moves to the condenser coil, which is located outside. As the gas passes through the condenser, it cools down and condenses back into a liquid. The heat absorbed from inside the building is released into the outdoor air.
Cooling Cycle Repeats:
The cooled liquid refrigerant is then allowed to expand through the expansion valve, which lowers its pressure and temperature even more before it enters the evaporator coil to absorb heat again, repeating the cycle.
Summary of the Cooling Cycle:
Evaporation: Refrigerant absorbs heat from inside air and evaporates.
Compression: The refrigerant gas is compressed, increasing its pressure and temperature.
Condensation: The refrigerant releases heat outside and turns back into a liquid.
Expansion: The refrigerant loses pressure and temperature, preparing to absorb more heat.
This continuous cycle keeps the indoor air cool, while the air conditioner expels the absorbed heat to the outside.
Why the Process Works:
The cooling effect of air conditioning comes from the phase change of the refrigerant. When the refrigerant changes from a liquid to a gas (and vice versa), it absorbs and releases heat. This process of heat transfer is what makes your indoor ******* e cooler.
Energy Efficiency and Cooling:
The energy consumption of an air conditioner is largely dependent on how efficiently it can transfer heat from inside to outside. Modern air conditioners are designed to do this in the most efficient way possible, often using less energy than older models, thanks to improved refrigerants, better insulation, and optimized components.
The temperature setting on the thermostat controls how long the air conditioner runs. For example, setting it at a cooler temperature requires the system to work harder to keep the room cool, using more energy.
In Summary:
Air conditioners work by using a refrigerant that absorbs heat from the indoor air, turning it into a gas, then compressing and cooling that gas to release the heat outdoors. The system circulates cool air back into the ******* e, keeping things comfortable.
EUTS impact on EU economic and is it working as expected or not
https://www.skuld.com/topi...

EU Emission Trading System - smooth sailing a half year into 2024? - Skuld
Since 1 January 2024, the EU Emission Trading System (ETS) Directive applies to maritime transport.
https://www.skuld.com/topics/environment/air-pollution/europe/eu-emission-trading-system---smooth-sailing-a-half-year-into-2024/Cargo fumigation at sea is a process used to control pests in cargo holds during transit. Here’s an overview of the rules and risks involved:
Rules:
International Standards: Fumigation must comply with international conventions such as the International Maritime Organization (IMO) guidelines and the International Plant Protection Convention (IPPC) regulations.
Documentation: Proper documentation and certification are required. This includes the fumigation certificate and a detailed plan of the fumigation process.
Safety Measures: The fumigation process must adhere to safety guidelines to protect crew members and the environment. This includes following safety procedures for handling and exposure to toxic gases.
Ventilation: Cargo holds must be properly ventilated before and after fumigation to ensure that toxic gases are cleared from the **** e before crew access.
Training: Personnel involved in fumigation must be trained and certified in handling fumigants and understanding the risks.
Risks:
Health Hazards: Fumigants are often toxic. Exposure to these chemicals can pose serious health risks to crew members, including respiratory issues, skin irritation, and other acute effects.
Environmental Impact: Improper handling or leakage of fumigants can harm marine life and the environment. Fumigants need to be managed carefully to prevent pollution.
Fire and Explosion: Some fumigants are flammable or can create explosive mixtures. Proper handling and storage are crucial to prevent accidents.
Legal Consequences: Non-compliance with regulations can lead to legal penalties and fines. It’s essential to adhere to all regulatory requirements and guidelines.
Effectiveness: There’s a risk that fumigation may not completely eradicate pests if not done correctly, leading to potential damage to the cargo.
Cargo fumigation at sea requires strict adherence to regulations and safety protocols to mitigate these risks and ensure the safety of both the crew and the environment.
Here's a list of different types of ships, along with descriptions of their functions. I can generate an image to showcase these ships together:
1. Container Ship
Function: These ships are designed to carry standardized cargo containers, which can easily be loaded, unloaded, and stacked. They are the backbone of global trade, transporting goods across the world.
2. Bulk Carrier
Function: Bulk carriers are used to transport large quantities of unpackaged bulk cargo, such as grains, coal, ore, and cement. They have large cargo holds to accommodate loose materials.
3. Tanker
Function: Tankers are designed to carry liquid cargo, such as crude oil, chemicals, or liquefied natural gas (LNG). They have specialized tanks to safely transport hazardous or volatile liquids.
4. Ro-Ro Ship (Roll-On/Roll-Off)
Function: Ro-Ro ships are designed to carry wheeled cargo, such as cars, trucks, trailers, and railroad cars. Vehicles are driven on and off the ship using ramps, making loading and unloading efficient.
5. Passenger Ship (Cruise Ship)
Function: Passenger ships, including cruise ships, are designed to transport people rather than cargo. Cruise ships offer luxury amenities and travel to tourist destinations, while ferries provide shorter trips.
6. Naval Ship
Function: Naval ships are military vessels designed for warfare, patrolling, and defense. Types include aircraft carriers, destroyers, frigates, submarines, and patrol boats.
7. Fishing Vessel
Function: Fishing vessels are used for catching fish and other seafood. They vary in size from small boats to large trawlers that can operate in deep waters.
8. Research Vessel
Function: Research vessels are equipped with scientific equipment to conduct marine research. They are used for studying oceanography, marine biology, and environmental conditions.
9. LNG Carrier
Function: LNG carriers are specialized ships designed to transport liquefied natural gas. They have insulated tanks to keep the gas at very low temperatures during transport.
10. Dredger
Function: Dredgers are used to remove sediment, sand, and debris from the bottom of rivers, harbors, and other bodies of water. They help maintain waterways and create new land.
11. Icebreaker
Function: Icebreakers are designed to navigate through ice-covered waters, clearing paths for other ships. They are equipped with reinforced hulls to break through thick ice.
12. Yacht
Function: Yachts are private luxury vessels used for leisure and recreation. They range from small sailing yachts to large motor yachts with opulent accommodations.
13. Barge
Function: Barges are flat-bottomed vessels used to transport goods, typically on rivers and canals. They are often towed or pushed by tugboats and are ideal for transporting heavy cargo.
14. Ferry
Function: Ferries transport passengers, vehicles, and cargo across bodies of water. They operate on fixed routes, providing a critical link between islands and mainland or across rivers.
15. LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) Carrier
Function: These specialized ships transport LNG in liquid form. They have heavily insulated tanks that keep the gas at -162°C to maintain its liquid state during transportation.
16. Tugboat
Function: Tugboats are small, powerful vessels used to maneuver larger ships into docks, through narrow waterways, or out of harbors. They are essential for guiding ships safely.
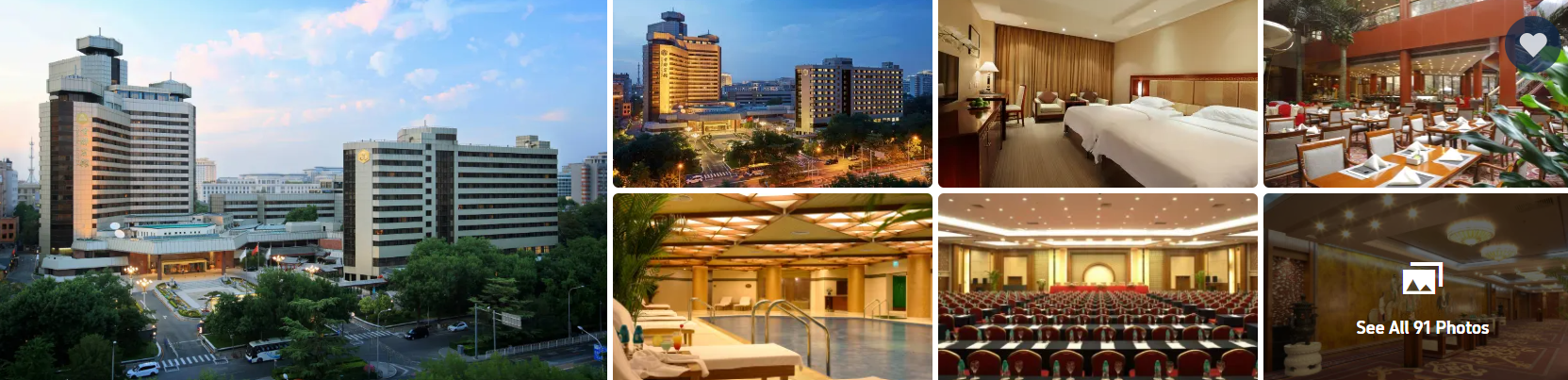
Property Description
Opened: 1989
Renovated: 2007
Number of Rooms: 588
Capital Hotel is a comprehensive five-star hotel in the central downtown area of Beijing. In the west of the hotel locates the Dongjiaominxiang Alley while in the north locate the Forbidden City and ****** fujing business district. It’s close to many scenic spots including Qianmen and Tiananmen. It is also surrounded by many government agencies and office buildings. With subways and bus stops nearby, the hotel is easily accessible.
Capital Hotel consists of two Towers. Tower A was open in 1989 and Tower B in 2007. Upon the completion of the Hotel Exterior Upgrading in May, 2018, Capital Hotel features landscaped gardens with traditional Chinese cultural ingredients including exquisite bridges, waterfalls and pavilions in the city center. The total green area reaches more than 5000㎡, not only brings diverse delights with elegant environment but also makes the guests stay more convenient.
While providing high-quality services, Capital Hotel has been strictly implementing the local epidemic prevention requirements, strengthening the prevention and control measures for everyone who enters the hotel, such as wearing masks, temperature detection, checking Health-kit, comprehensive cleaning and sterilization, regular nucleic acid testing for raw materials and personnel, keeping safe distance for meetings and banquets, so as to make your stay more safe and pleasant.
With prime location, state of the art facilities, regular epidemic prevention and control measures, capital hotel makes it a safe, comfortable and professional place for leisure, business and conferences.
https://prf.hn/l/BJlLlVJ
Maxwell Reserve Singapore, Autograph Collection
Property Description
Opened: 2021
Number of Rooms: 127
Located in downtown Singapore in Murray Terrace, a 100 year old British colonial building, Maxwell Reserve is a masterpiece envisioned by owner Satinder Garcha and executed by the world renowned French designer Jacques Garcia that elegantly embodies decadent European grandeur infused with cosmopolitan sophistication. Standing true to its values of Roots, Glory and Pride, Maxwell Reserves takes pride to indulge its guests in emotional hospitality in its rich fun-filled environment, adorned with the owner's museum quality family artifacts dating all the way back to 1709, that illustrate Garcha's passion for Polo and the glorious history of Singapore and Royal India.
https://prf.hn/l/de4xVQw

The IAPH Environmental Ship Index enters in a new era - SAFETY4SEA
ESI entered a new era in March, with the confirmation of an expanded suite of performance modules to support ports and vessel owners.
https://safety4sea.com/the-iaph-environmental-ship-index-enters-in-a-new-era/



